Vulnerability Test Singapore
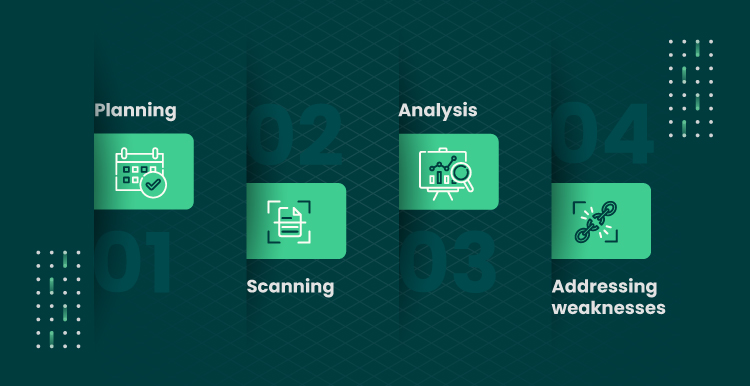
Executive Summary
Vulnerability testing is a critical cybersecurity measure that helps organizations identify and remediate vulnerabilities in their systems and software. In Singapore, with its rapidly growing digital landscape, organizations face an increasing risk of cyberattacks. Vulnerability testing is essential for businesses to protect their data, reputation, and financial well-being.
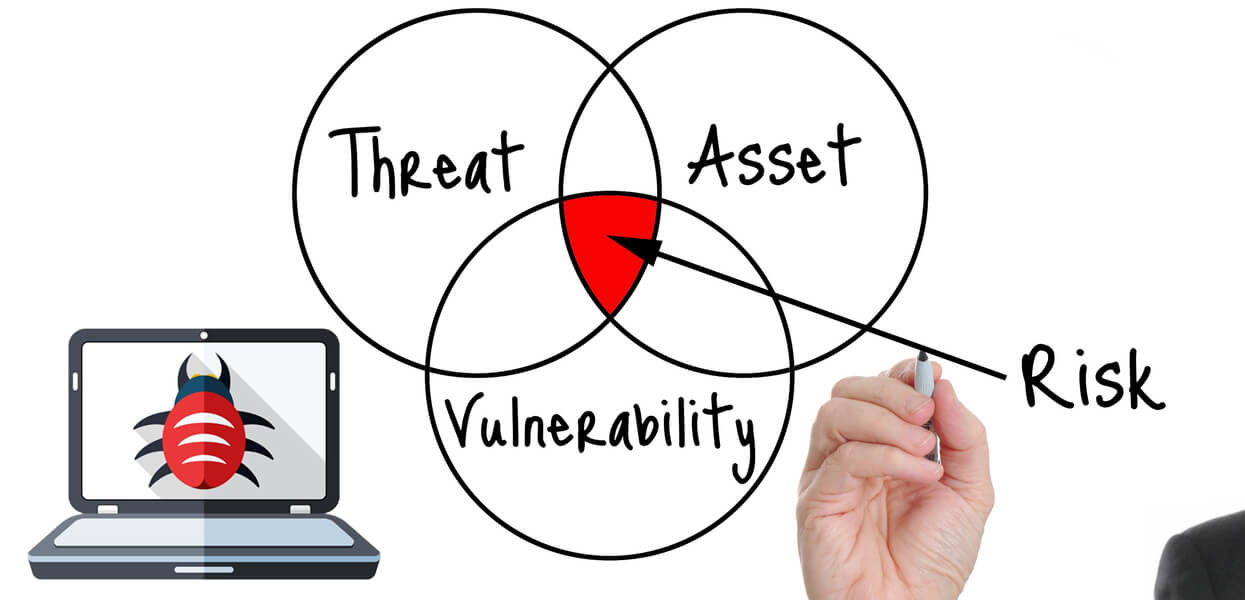
Introduction
Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent, making it crucial for organizations to implement robust security measures to protect their systems and data. Vulnerability testing is a vital component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, as it helps organizations identify and address potential weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
FAQs
- What is vulnerability testing?
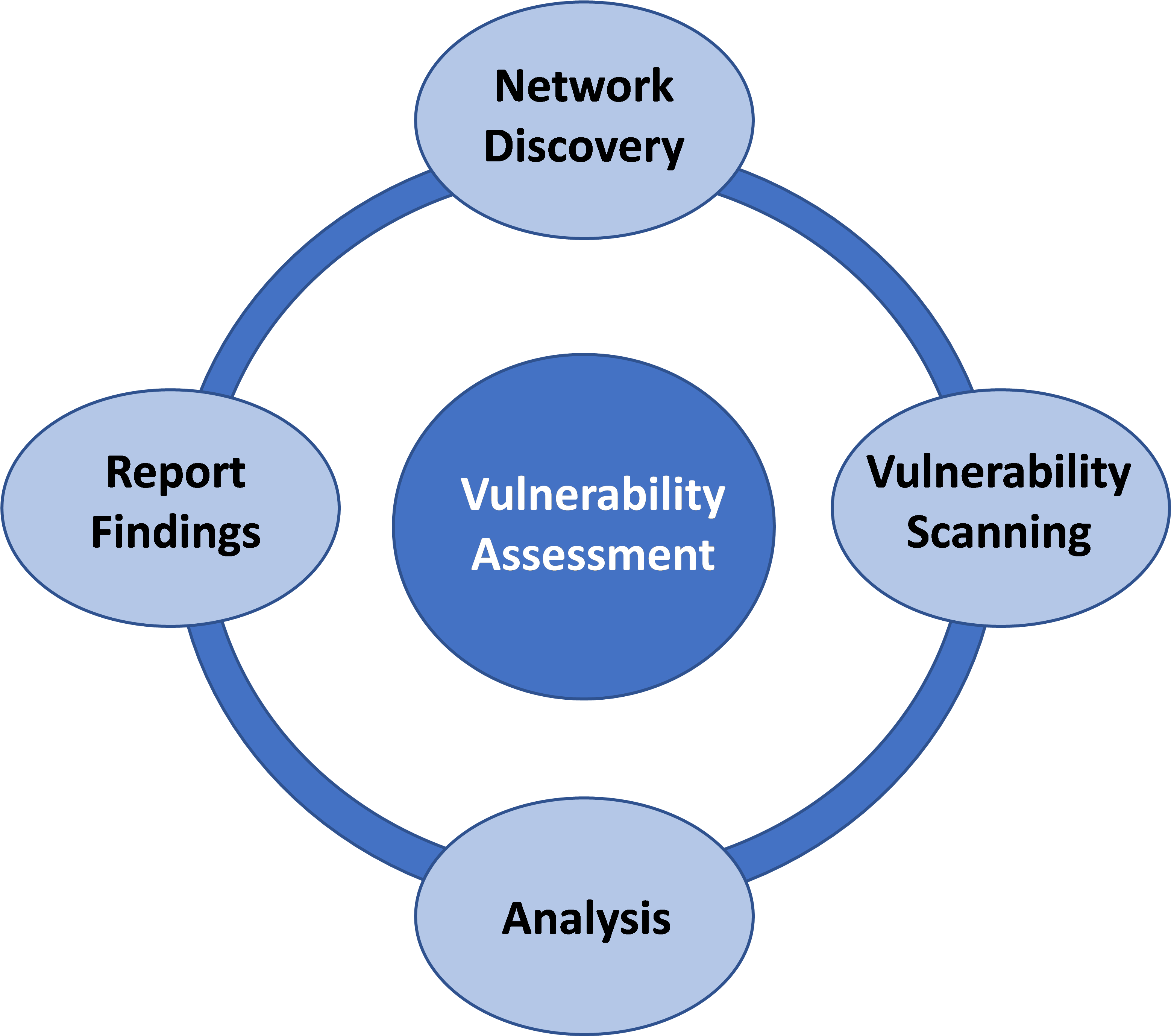
Vulnerability testing is the process of identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and applications. These vulnerabilities can arise from software bugs, configuration errors, or outdated software versions, and can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or disrupt operations.
- Why is vulnerability testing important for Singaporean organizations?
Singapore is a highly connected and technologically advanced society, with a growing number of businesses and individuals relying on digital platforms for various activities. This increased digital connectivity has also made organizations more vulnerable to cyberattacks, making vulnerability testing essential for protecting their assets and reputation.
- How often should vulnerability testing be conducted?
The frequency of vulnerability testing depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of an organization’s IT infrastructure, the industry it operates in, and the level of cybersecurity risk it faces. Generally, it is recommended to conduct vulnerability tests on a regular basis, such as quarterly or semi-annually, or more frequently in high-risk environments.
Types of Vulnerability Testing
Network Penetration Testing
Network penetration testing simulates real-world attacks by attempting to exploit vulnerabilities in the organization’s network infrastructure, including firewalls, routers, and servers.
- External Penetration Testing: Tests from outside the network to identify vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit remotely.
- Internal Penetration Testing: Tests from within the network to identify vulnerabilities that insiders or unauthorized users could exploit.
Web Application Penetration Testing
Web application penetration testing targets vulnerabilities in web applications that are accessible via the Internet.
- Black-box Testing: Tests without any prior knowledge of the web application’s code or structure.
- White-box Testing: Tests with full knowledge of the web application’s code and structure.
Mobile Application Penetration Testing
Mobile application penetration testing evaluates vulnerabilities in mobile applications that run on smartphones and tablets.
- Android Penetration Testing: Tests for vulnerabilities in Android-based mobile applications.
- iOS Penetration Testing: Tests for vulnerabilities in iOS-based mobile applications.
Cloud Penetration Testing
Cloud penetration testing assesses the security of cloud environments, including virtual machines, storage, and networking resources.
- Public Cloud Penetration Testing: Tests public cloud services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Private Cloud Penetration Testing: Tests private cloud environments deployed on-premises or hosted by a managed service provider.
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) Penetration Testing
ICS penetration testing is designed for critical infrastructure systems, such as those used in utilities, manufacturing, and transportation.
- SCADA Systems Penetration Testing: Tests for vulnerabilities in Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems that control industrial processes.
- PLC Systems Penetration Testing: Tests for vulnerabilities in Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) that control industrial automation.
Benefits of Vulnerability Testing
- Enhanced Security Posture: Vulnerability testing helps organizations identify and remediate vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of successful cyberattacks.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Many industry regulations and standards require organizations to conduct vulnerability tests regularly.
- Reputation Protection: A successful cyberattack can damage an organization’s reputation and lead to loss of trust from customers and partners.
- Reduced Financial Losses: Data breaches and cyberattacks can result in significant financial losses for organizations.
- Enhanced Employee and Customer Confidence: Vulnerability testing demonstrates that an organization is taking proactive steps to protect sensitive data and personal information.
Conclusion
Vulnerability testing is a critical cybersecurity measure that helps organizations in Singapore protect themselves from the growing threat of cyberattacks. By identifying and remediating vulnerabilities in their systems and software, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches, reputational damage, and financial losses. Regular vulnerability testing should be an integral part of any comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, allowing organizations to maintain a strong security posture and protect their valuable assets.
Keywords: Vulnerability Testing Singapore, Cybersecurity, Network Penetration Testing, Web Application Penetration Testing, Cloud Penetration Testing
