Vulnerability Test
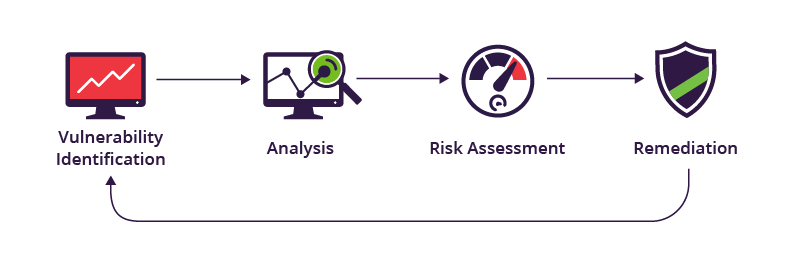
A vulnerability test is a security assessment that identifies weaknesses in a computer system, network, or application that could be exploited by attackers. The goal of a vulnerability test is to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities that need to be fixed in order to improve the security posture of the system.
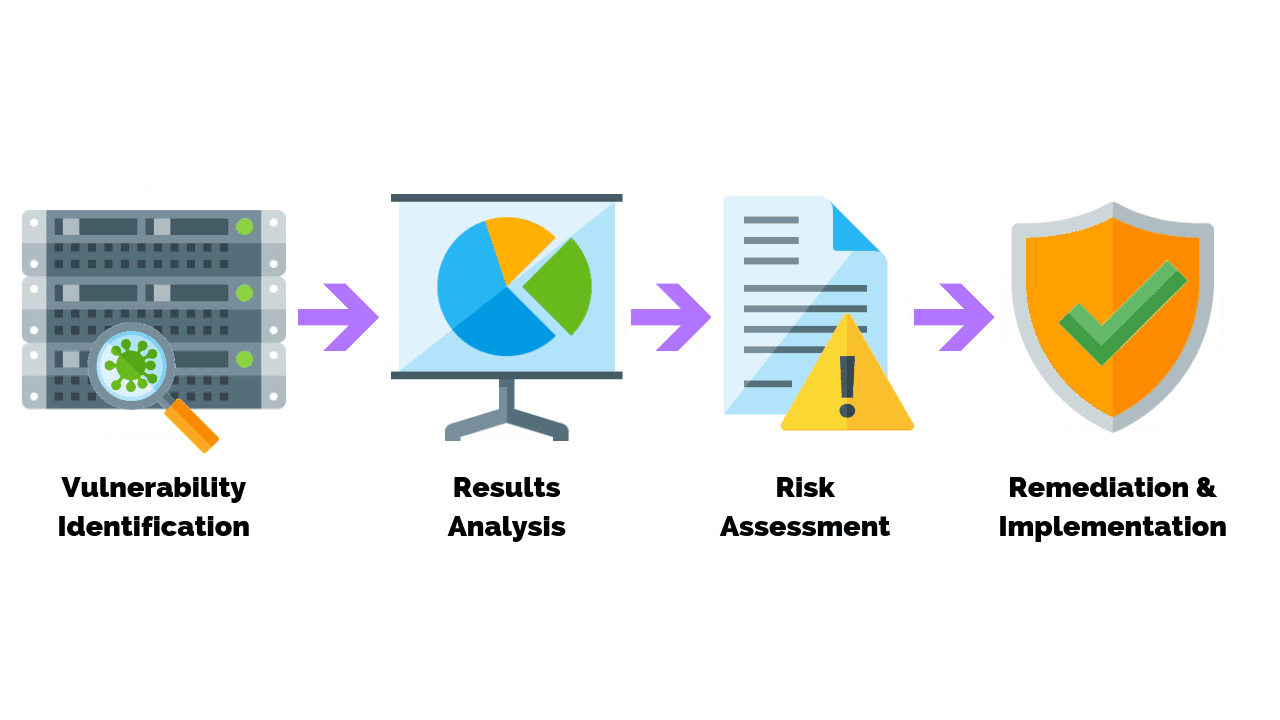
There are two main types of vulnerability tests:
- Static vulnerability tests analyze the code of a system or application to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Dynamic vulnerability tests test a running system or application to identify vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
Vulnerability tests can be performed manually or with automated tools. Manual vulnerability tests are more time-consuming and expensive, but they can provide more detailed information about the vulnerabilities. Automated vulnerability tests are faster and less expensive, but they can sometimes miss vulnerabilities that manual tests would identify.
The results of a vulnerability test are typically presented in a report that lists the vulnerabilities that were identified, along with their severity and recommended remediation steps. The report should also provide an overall assessment of the security posture of the system.
Vulnerability tests are an important part of any comprehensive security program. They can help organizations to identify and fix vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.## Vulnerability Test
Executive Summary
Vulnerability testing is a crucial cybersecurity practice that helps organizations identify and remediate vulnerabilities within their systems and networks. This article provides a comprehensive overview of vulnerability testing, its types, methodologies, and best practices, empowering organizations to effectively protect their digital assets and maintain a robust security posture.
Introduction
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, organizations face an ever-evolving threat landscape. Vulnerabilities, whether inherent in software or arising from configuration errors, can provide entry points for malicious actors to exploit and gain unauthorized access to systems and data. Vulnerability testing plays a vital role in proactively detecting and mitigating these vulnerabilities, enabling organizations to enhance their cybersecurity posture and reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is vulnerability testing?
Vulnerability testing involves the systematic identification and analysis of weaknesses within an organization’s IT systems and networks that could potentially be exploited by attackers.
Q2. Why is vulnerability testing important?
Regular vulnerability testing helps organizations:
- Proactively identify and prioritize critical vulnerabilities
- Understand the potential impact of vulnerabilities on their systems and data
- Develop targeted mitigation strategies to reduce risk
Q3. Who conducts vulnerability testing?
Vulnerability testing can be conducted by organizations themselves using internal resources or by hiring third-party cybersecurity firms that specialize in this service.
Top 5 Subtopics
1. Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning is an automated process that uses tools to scan systems and networks for known vulnerabilities.
- Detects vulnerabilities based on predefined signatures or pattern matching
- Identifies vulnerable software, operating systems, and network configurations
- Provides detailed reports with vulnerability severity ratings and remediation recommendations
2. Penetration Testing
Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities that automated tools may miss.
- Involves ethical hackers using various techniques to exploit vulnerabilities
- Tests the effectiveness of security controls and uncovers potential attack paths
- Provides detailed reports outlining the vulnerabilities identified and potential remediation measures
3. Risk Assessment
Risk assessment evaluates the potential impact and likelihood of vulnerabilities.
- Analyzes vulnerability scan and penetration test results to determine the severity of identified vulnerabilities
- Prioritizes vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on business operations and data security
- Provides recommendations for mitigation and remediation strategies
4. Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management involves the ongoing process of identifying, assessing, and remediating vulnerabilities throughout an organization’s IT infrastructure.
- Establishes a systematic approach to vulnerability handling
- Includes vulnerability monitoring, patching, and regular testing
- Ensures that identified vulnerabilities are quickly addressed to minimize the risk of exploitation
5. Best Practices for Vulnerability Testing
- Regularly conduct vulnerability scans and penetration tests to maintain a comprehensive understanding of vulnerabilities
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on risk and business impact
- Implement a vulnerability management program to ensure timely remediation
- Stay updated on the latest vulnerabilities and threat landscape
- Train staff on vulnerability awareness and secure practices
Conclusion
Vulnerability testing is an indispensable cybersecurity measure that enables organizations to proactively identify and mitigate vulnerabilities within their IT systems and networks. By incorporating this practice into their security strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks, protect their sensitive data, and maintain a robust security posture.
Relevant Keyword Tags
- Vulnerability Management
- Vulnerability Testing
- Risk Assessment
- Penetration Testing
- Cybersecurity Best Practices
