PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)

PCI DSS is a set of security standards established to ensure that all companies that process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. Compliance with PCI DSS is required for all merchants, service providers, and payment processors that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card data. Failure to comply with PCI DSS can result in fines, penalties, and loss of access to the payment card processing system.

The PCI DSS consists of 12 core requirements:
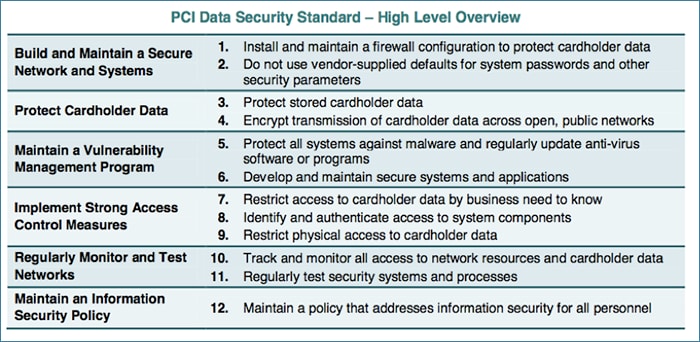
- Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data.
- Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters.
- Protect stored cardholder data.
- Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open public networks.
- Use and regularly update anti-virus software or programs.
- Develop and maintain secure systems and applications.
- Restrict access to cardholder data by business need-to-know.
- Assign a unique ID to each person with computer access.
- Restrict physical access to cardholder data.
- Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data.
- Regularly test security systems and processes.
- Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel.
In addition to these core requirements, PCI DSS also includes several additional requirements that vary depending on the size and complexity of the merchant’s business. For example, merchants that process large volumes of transactions may be required to implement additional security measures, such as intrusion detection and prevention systems, and fraud detection and prevention systems.## PCI DSS
Executive Summary
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards that aim to protect cardholder data from theft, fraud, and misuse. It is a comprehensive framework that addresses all aspects of cardholder data security, from data acquisition and storage to transmission and disposal. PCI DSS compliance is mandatory for all merchants and service providers that accept, transmit, or store cardholder data.
Introduction
PCI DSS was developed by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), a global organization that is responsible for the development and maintenance of the standard. The first version of PCI DSS was released in 2024, and it has been updated several times since then to keep pace with the evolving threats to cardholder data security.
PCI DSS is a complex and technical standard, but it is essential for merchants and service providers that accept, transmit, or store cardholder data. Compliance with PCI DSS helps to protect cardholder data from theft, fraud, and misuse, and it can help businesses to avoid the costly fines and penalties that can result from a data breach.
FAQs
What is PCI DSS?
PCI DSS is a set of security standards that aim to protect cardholder data from theft, fraud, and misuse.
Who is required to comply with PCI DSS?
All merchants and service providers that accept, transmit, or store cardholder data are required to comply with PCI DSS.
What are the benefits of PCI DSS compliance?
PCI DSS compliance helps to protect cardholder data from theft, fraud, and misuse, and it can help businesses to avoid the costly fines and penalties that can result from a data breach.
Subtopics of PCI DSS
Requirement 1: Install and Maintain a Firewall Configuration to Protect Cardholder Data
- Firewall: A network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Implementation of a firewall can block unauthorized access to cardholder data by creating a barrier between the internal network and external networks.
Requirement 2: Do Not Use Vendor-Supplied Default Security Parameters
- Default Security Parameters: Predefined security settings provided by the vendor and often used to simplify the initial setup. Leaving these default settings unchanged can create security vulnerabilities and compromise the confidentiality of cardholder data.
Requirement 3: Protect Stored Cardholder Data
- Data Encryption: Encrypting cardholder data makes it unreadable to unauthorized individuals, even if they gain access to the data. Encryption can be used to protect data both at rest and in transit.
Requirement 4: Encrypt Transmission of Cardholder Data Across Open, Public Networks
- Encryption: The process of converting plaintext data into ciphertext using an encryption algorithm and key. Encrypting data in transit helps protect cardholder data from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Requirement 5: Use and Regularly Update Anti-Virus Software
- Anti-Virus Software: Software designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans, from infecting a computer system.
Conclusion
PCI DSS is a comprehensive and technical standard that can help businesses to protect cardholder data from theft, fraud, and misuse. Compliance with PCI DSS is essential for businesses that accept, transmit, or store cardholder data, and it can help businesses to avoid the costly fines and penalties that can result from a data breach.
Keywords
- PCI DSS
- Cardholder data security
- Data protection
- Compliance
- Payment security
